All Rights Reserved Privacy Policy Site Map
FOCUS ON EC FAN ONLY
FOCUS ON EC FAN ONLY
In the field of ventilation equipment, cross-flow fans and centrifugal fans are two common types of fans, which play a significant role in various scenarios such as industrial production, household appliances, and commercial buildings. Although both undertake the task of gas transportation, due to the differences in working principles and structural designs, there are significant differences in performance parameters and application scenarios.

The cross-flow fan, also known as the tangential blower, has a unique working principle that air passes through the impeller twice. Its impeller is generally multi-bladed and long cylindrical in shape, without front and rear discs. When the impeller rotates, the airflow enters the blade grid from the open part of the impeller, passes through the interior of the impeller, and is discharged from the other side of the blade grid, forming an airflow movement through the impeller, just like water flowing through a water pipe. This special working mode enables it to generate uniform and flat airflow.
The working principle of a centrifugal fan is based on centrifugal force. The impeller of the fan rotates at high speed driven by the electric motor. The gas filling the blade channels is thrown from the center of the impeller to the outer edge of the impeller under the action of centrifugal force, the pressure rises, and it leaves the impeller at high speed and enters the volute. In the volute, the gas decelerates as the flow channel gradually expands, and part of its kinetic energy is converted into static pressure energy. Finally, it is discharged from the fan tangentially. When the gas in the impeller is discharged, a negative pressure is formed at the center of the impeller. Under the action of atmospheric pressure, the outside gas enters the impeller and continuously conveys the gas.
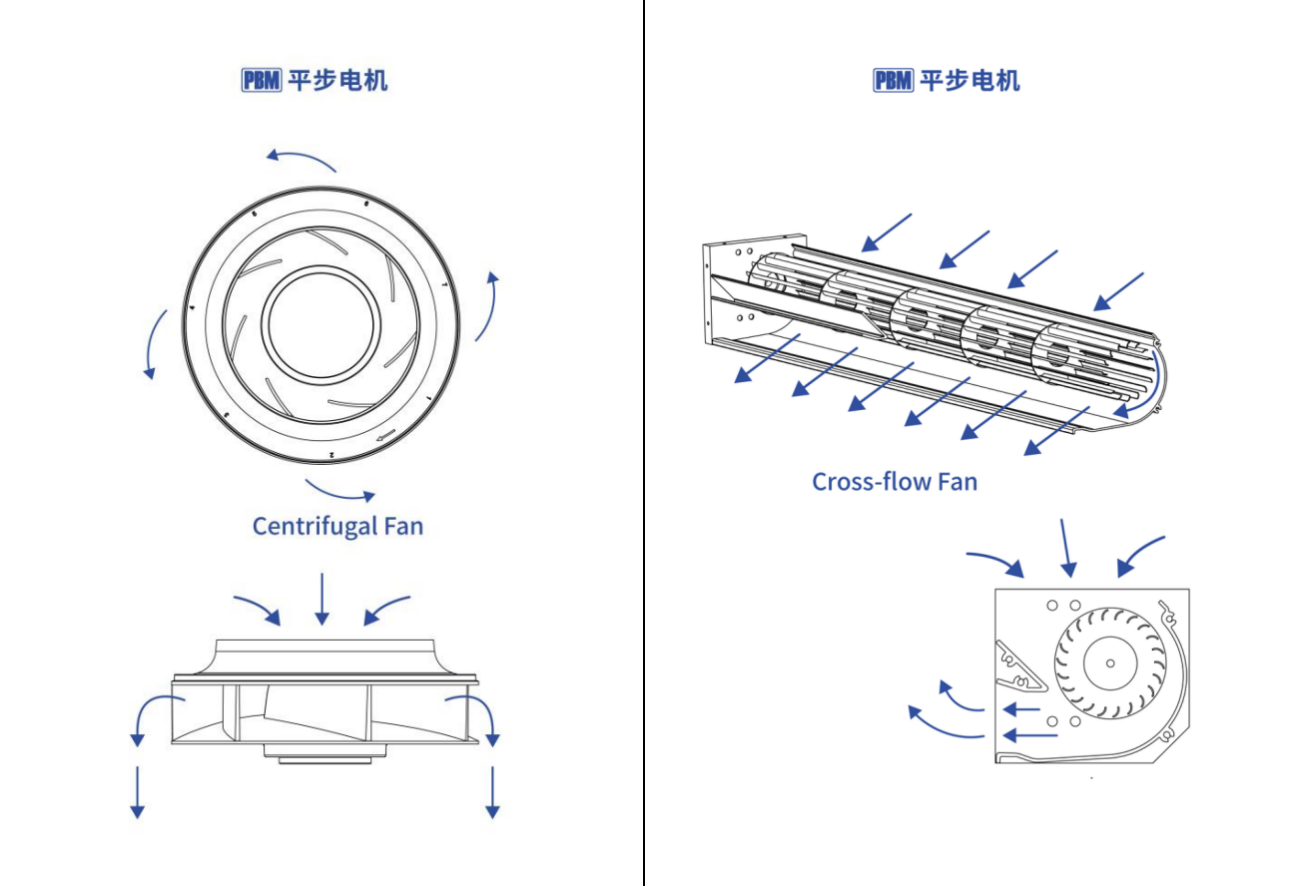
2. Performance parameters
A. Air volume: Air volume refers to the volume of gas conveyed by the fan within a unit of time, and the unit is usually cubic meters per hour (m³/h). Due to its structural features, the cross-flow fan has a uniform air distribution and can generate a large air volume. However, the air volume range of a single fan is usually relatively small. The air volume of the cross-flow fan commonly used in the indoor units of household air conditioners is generally between 300 and 1500m³/h. The air volume range of centrifugal fans is much broader. The air volume of small centrifugal fans may only be a few dozen cubic meters per hour, while that of large industrial centrifugal fans can reach several hundred thousand cubic meters per hour.
b. Wind pressure: Wind pressure is used to measure the ability of a fan to overcome resistance, with the unit being PASCAL (Pa). The wind pressure of a cross-flow fan is relatively low, generally ranging from tens to hundreds of pascals. This is because its unique airflow movement pattern causes significant energy loss during the gas flow process. Centrifugal fans have obvious advantages in generating air pressure and can produce relatively high air pressure. The air pressure range of medium and low-pressure centrifugal fans is generally 98 to 1470Pa, while that of high-pressure centrifugal fans can exceed 3000Pa. They are suitable for ventilation systems that need to overcome significant resistance.
c. Rotational speed: Rotational speed refers to the number of rotations of the fan impeller per minute, with the unit being revolutions per minute (r/min). To ensure the stability and uniformity of the airflow, the rotational speed of the cross-flow fan is relatively low, generally ranging from 800 to 2000r/min. The rotational speed range of centrifugal fans is relatively wide. The rotational speed of small centrifugal fans may be between 1000 and 3000r/min, while large centrifugal fans, due to their larger size, have relatively lower rotational speeds to ensure operational stability, around several hundred revolutions per minute.
d. Efficiency: The efficiency of a fan reflects its ability to convert input power into effective power. Generally speaking, centrifugal fans have a relatively high efficiency under design conditions, reaching 70% to 90%, which is attributed to their relatively mature design and stable airflow movement mode. Due to the complex flow of air within the impeller, cross-flow fans suffer significant energy loss and have relatively low efficiency, typically ranging from 30% to 60%.
3. Application scenarios
Due to the characteristics of large air volume, uniform airflow and compact structure of cross-flow fans, they are widely used in household appliances, such as indoor units of air conditioners, air curtains and warm air fans. In the indoor unit of an air conditioner, the cross-flow fan can evenly blow out the cold air generated by the evaporator, achieving the circulation of indoor air and temperature regulation. The air curtain can form a uniform air curtain by using a cross-flow fan, effectively blocking the exchange of cold and hot air between the indoor and outdoor, and playing a role in energy conservation and dust isolation.
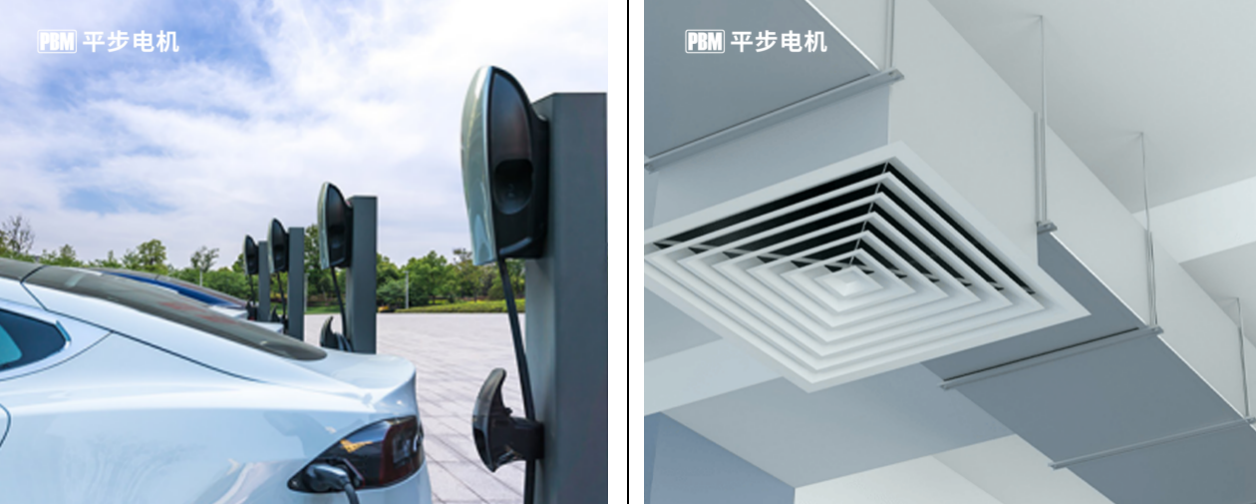
Centrifugal fans, with their advantages of high air pressure and wide air volume range, occupy an important position in fields such as industrial ventilation, air conditioning systems, and dust removal equipment. In industrial plants, centrifugal fans are used to remove harmful gases and dust to ensure the air quality inside the plants. In large-scale central air conditioning systems, centrifugal fans can overcome pipeline resistance and achieve long-distance air transportation. In dust removal equipment, the centrifugal fan provides sufficient air pressure to allow the dusty gas to pass through the dust removal device, achieving the separation of dust and gas.

4. Advantages and Disadvantages
Advantages of cross-flow fans: Compact structure and small space occupation; The airflow is uniform and can form a flat airflow, making it suitable for occasions with high requirements for airflow uniformity. The operating noise is relatively low, making it suitable for home use and environments sensitive to noise.
Disadvantages of cross-flow fans: They have relatively low air pressure and are not suitable for long-distance transportation or situations where significant resistance needs to be overcome. The efficiency is relatively low and the energy consumption is high. The air volume of a single fan is limited and it is difficult to meet the demands of large air volume and high air pressure.
Advantages of centrifugal fans: High air pressure, capable of overcoming significant resistance and achieving long-distance gas transportation. The air volume range is wide, which can meet the ventilation requirements of different scales. It has high efficiency and good energy-saving effect. The technology is mature, with a rich variety of products and strong selectivity.
Disadvantages of centrifugal fans: relatively complex structure, large volume, and occupy a lot of space. The noise is relatively high during operation and sound insulation measures need to be taken. The price is relatively high, especially for large high-pressure centrifugal fans.
By continuing to use the site you agree to our privacy policy Terms and Conditions.